Local privilege escalation in Windows OS through installed EPSON printers installed in non-English language
Vulnerability Reference: CVE-2025-42598
Description:
If a user performs either of the following actions:
- Installs an Epson Windows Printer Driver in non-English OS environments
- Changes the language to one other than English
It is possible to overwrite some DLL files managed by the printer driver with all account privileges.
Impact:
A third party may be able to execute arbitrary code to allow higher privilege access and escalation capabilities. There are currently no reports of attacks exploiting this vulnerability.
Solution:
To ensure the security of your Epson product, please run the Epson Software Updater or download and install the Security vulnerability patch.
As a general rule, to help secure all devices, end-users and their administrators should always implement and maintain industry-standard security controls and practices in setting up and managing their networks.
For more information on securing your Epson product visit our Security Guidebook.
The Software Patch supports the following Operating Systems:
Windows® XP/XP Professional x64 Edition
Windows® Vista/Vista x64 Edition
Windows® 7/7 x64
Windows® 8/8 x64
Windows® 8.1/8.1 x64
Windows® 10/10 x64
Windows® 11 x64
Windows® Server 2003
Windows® Server 2008/2008 R2
Windows® Server 2012/2012 R2
Windows® Server 2016
Windows® Server 2019
Windows® Server 2022
Windows® Server 2025
For those not yet using Epson Software Updater
Step 1 - Download Epson Software Updater from the local Epson support page.
Step 2 - Download the patch software via Epson Software Updater and then run it.
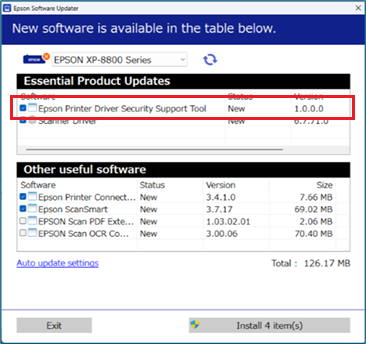
For users already using Epson Software Updater
Run the Epson Software Updater and install the Epson Printer Driver Security Support Tool.
Epson Printer Driver Security Support Tool
For devices where software updater is not available, please download and install the Epson Printer Driver Security Support Tool (click on the link below).
Epson Printer Driver Security Support Tool
Credit
We would like to thank private security researcher Erkan Ekici for his extensive work in identifying and sharing this security issue with us.